Texas: CWD Positive
Unfortunately, white-tailed deer hunting, management and Chronic Wasting Disease (CWD) now go hand-in-hand in Texas. It’s something that wildlife officials, hunters and deer herds are dealing with across the country. Texas and many states have been sampling hunter-harvested deer to find out more about where the deadly disease is and is not. The end game is far from unknown.
CWD Sampling in Texas
The 2016-17 collection year resulted in a couple of unwanted firsts for CWD in Texas, including detections in a free-ranging whitetail and a free-ranging elk. The Texas Parks and Wildlife Department (TPWD) surpassed its statewide goal of 6,735 CWD samples, collecting 9,830 from hunter harvested and road kill deer, and other susceptible cervid species, between March 1, 2016 and Feb. 28, 2017.
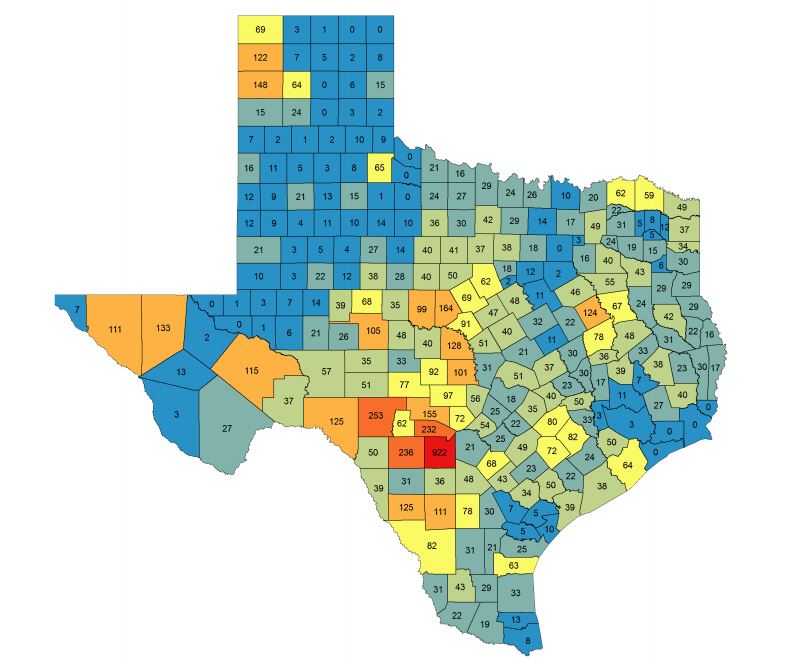
Sampling by DMUs
Sampling objectives were established by TPWD wildlife biologists based on deer densities within each of the 41 Deer Management Units (DMU) in Texas and other factors to establish sufficient confidence of detection if CWD were present within those localized populations.
TPWD wildlife staff collected CWD samples from a variety of locations including: road kill deer, deer processors, private ranches, wildlife management areas and state parks, and voluntary and mandatory hunter harvest check stations. Of the 9,830 samples collected, 23 percent were road kill. Exotic species that have been sampled include axis deer, fallow deer, red stag, sika, and elk; although there is no evidence that axis and fallow deer are susceptible to this disease.
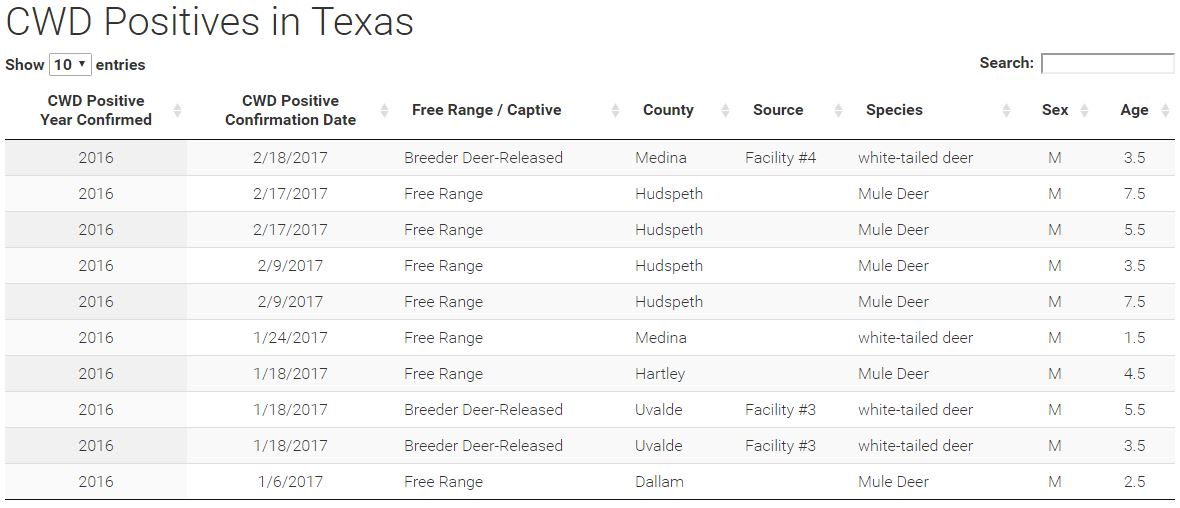
Details about each CWD detection in Texas are available online. Just click on the image below to find out more.
Texas’ CWD First
Sometimes it’s good to have firsts—sometimes it’s not. Among the CWD positives detected in Texas this past season, here are some notable firsts:
- The first confirmed case of CWD in a free-ranging Texas whitetail was detected in a hunter harvested 1 1/2 –year-old buck submitted for sampling within the Surveillance Zone 3 located in portions of Medina, Uvalde, and Bandera counties.
- The first known free-ranging elk in Texas to test positive for CWD, harvested by a hunter in Dallam County.
- The first known case of a captive-raised white-tailed deer in Texas that live tested “not detected” for CWD, but after being harvested by a hunter on a release site three months later tested positive for the disease.
To date, Texas has recorded 49 confirmed cases of CWD, of which 26 were discovered in captive deer breeding pens, 5 were hunter harvested on breeder deer release sites, 16 were free-ranging mule deer, 1 was a free-ranging elk, and 1 was a free-ranging white-tailed deer.

CWD in West Texas
“The good news is so far our sampling in the Tran-Pecos has only detected CWD in the Hueco Mountains area,” said Dr. Bob Dittmar, TPWD wildlife veterinarian. “Since 2012, the disease has been found in 13 mule deer out of 117 tested in the Hueco Mountains area for an 11 percent prevalence rate.”
Dittmar also expressed guarded confidence that CWD has not spread outside the Hueco Mountains area based on increased sampling in the surrounding ranges.
“The mandatory sampling in the Trans-Pecos SZ helped get an increase in sampling from the Delaware Mountains this year and while we have accumulated a decent number of samples around the Guadalupe Mountains, both remain areas of concern and we still need some more sampling out there.” he noted.
CWD in Central Texas
The state’s wildlife disease management response focuses on an early detection and containment strategy designed to limit the spread of CWD from the affected area and better understand the distribution and prevalence of the disease.
The detection of CWD in a free-ranging whitetail in Medina County this season resulted from enhanced voluntary testing of hunter harvested deer, allowing TPWD to initiate proactive measures aimed at containment rather than reactive steps targeting control.
“The more effective we are at containing this disease within a limited geographic area, the better it will be for our wildlife resources and all those who enjoy them,” Dittmar said. “We want to thank the Texas hunting community for its strong support of our management efforts; we cannot combat the spread of CWD without it.”
A detailed summary of CWD sampling for 016-17 season is available for review online.